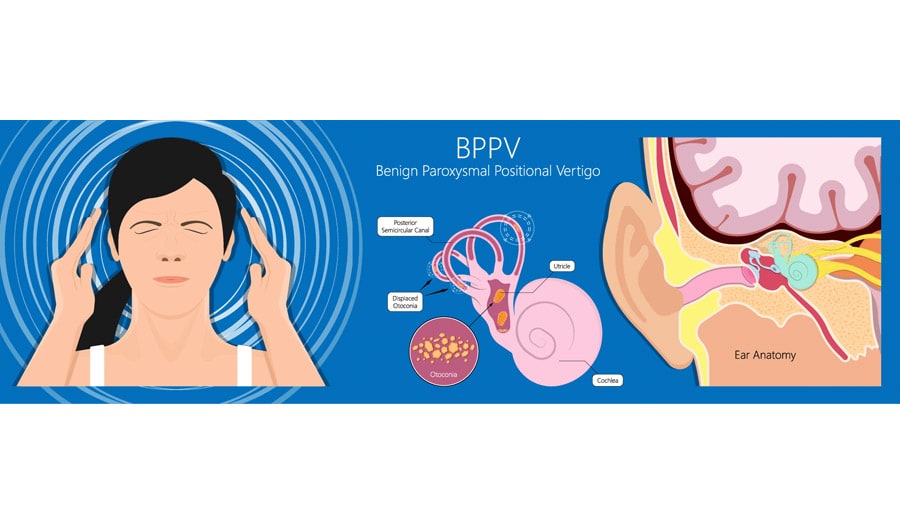
The ear nerve has a connection that goes to the eye muscles and can affect the person's ability to maintain gaze, focus and tolerate visual motion. If dysfunction is identified in this vestibular ocular mechanism, visual motor exercises including Custom designed APPs are used for gaze stabilization, eye head coordination, optokinetic, fusion, and visual motion.